中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (1): 62-67.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.01.010
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
兔骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养后的活力检测
孔根现1,2,蒋知新1,2,沙 杭2,张清华1,2
- 1南方医科大学研究生学院,广东省广州市 510515
2解放军第三○五医院老年病中心,北京市 100017
Isolation, culture and cell viability testing of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Kong Gen-xian1,2, Jiang Zhi-xin1,2, Sha Hang2, Zhang Qing-hua1,2
- 1 Postgraduate School, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
2 Geriatric Center, the 305 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100017, China
摘要:
背景:目前分离纯化骨髓间充质干细胞多采用单一的方法,对扩增培养过程中细胞活力的变化没有较为系统而全面的评估。
目的:探索体外分离培养和纯化兔骨髓间充质干细胞的方法,并对细胞的活力进行检测。
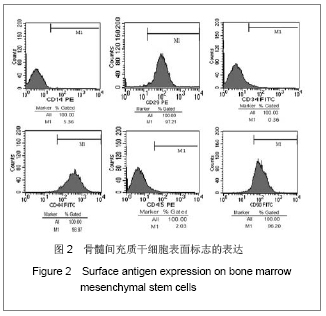
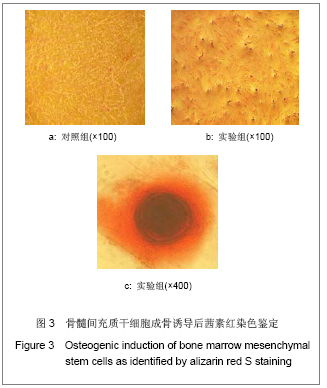
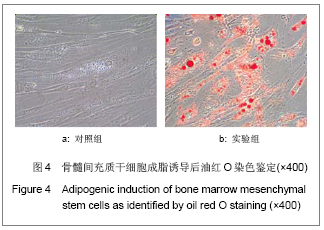
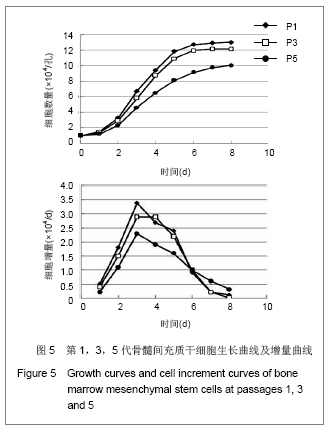
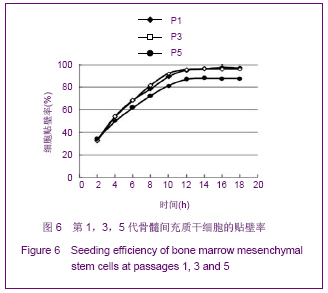
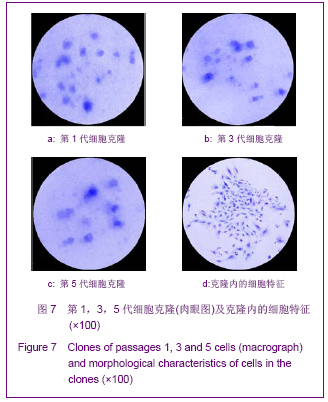
方法:采用密度梯度离心联合贴壁筛选的方法分离纯化兔骨髓间充质干细胞,从形态学、细胞表型和成骨成脂能力方面进行鉴定;并从细胞生长曲线、贴壁率和克隆形成率3个方面评估细胞活力。
结果与结论:原代细胞多呈梭形和圆形,48 h后大部分细胞贴壁,8-10 d细胞融合达80%-90%,传代周期为3-5 d;流式检测显示CD14、CD34和CD45表达阴性,CD29、CD44和CD90表达阳性;成骨诱导茜素红染色可见明显的钙结节,成脂诱导油红O染色可见大量脂肪细胞;细胞生长曲线、贴壁率及克隆形成率的结果表明第1代和第3代细胞的活力优于第5代细胞。结果说明密度梯度离心联合贴壁筛选的方法能够有效的分离纯化骨髓间充质干细胞,并能较好的保持其生物功能,在扩增传代过程中,细胞活力会有不同程度的下降。
中图分类号: